Drinking contaminated water can be very harmful to our health. It can cause diseases such as cholera; diarrhea, typhoid, dysentery, and guinea worm disease are a few of the common water-borne diseases. They are more widespread in remote areas that don’t have water purification systems.
While we dwelled on how to purify water, we found 12 easy and effective ways of filtering organic and inorganic impurities to make it safe for drinking. We are going to look at these most effective methods of water purification.
How to Purify Water by Removing Organic Impurities
1. Using Bleach/chlorine Disinfection
Chlorine is largely used in the purification of water in municipalities, giving safe drinking water to a city’s population. Household grade chlorine is commonly known as bleach, it is normally sold at a chlorine concentration of 4% to 6%, and that’s what is used to disinfect water and purify it.
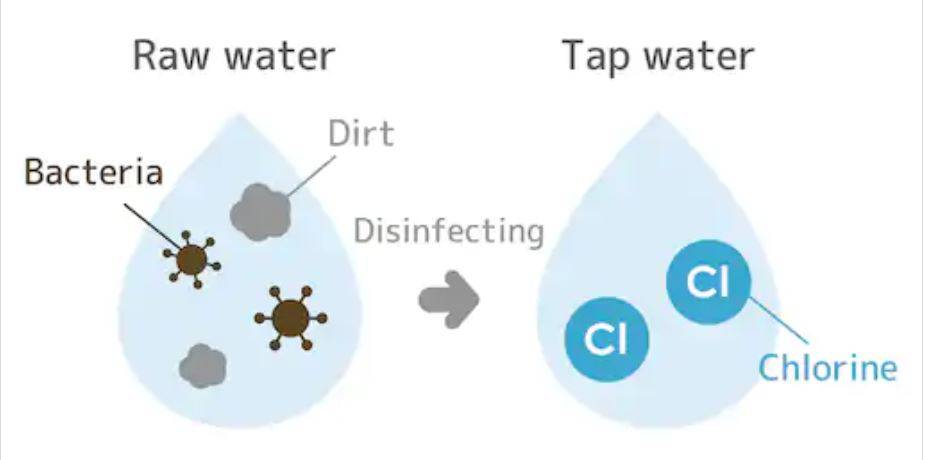
Sodium Hypochlorite (NaOCl) is the active ingredient in chlorine products. The concentration of sodium hypochlorite determines how chlorine is used.
Use eight drops of household bleach for every one gallon of water or two drops for every one liter of water. Leave it to stand for about 30 minutes before drinking.
Chlorine can also be found in pre-dosed tablets which are dropped into a water container and left to sit for about 45 minutes as the chemical starts to kill the pathogens, this method of purification removes Giardia, Bacteria, and Viruses. However, it does not remove Cyclosporum and Cryptosporidium.
2. UV Purification using Ultra Violet Light
The sun’s ultraviolet rays are very destructive to microorganisms. They are used to decontaminate the water from harmful pathogens and bacteria. Ultraviolet light has been a standard in disinfecting water supplies for decades at the municipal; however, it is currently being used in homes.
UV water purification is the most effective way of destroying pathogens from water sources because of the many contaminants that are powerless against ultraviolet radiation. Waterborne viruses, bacteria, parasites, and molds are all defenseless when they go through ultraviolet light.
UV purification systems generate much UV light compared to the sun; hence, they are tougher than solar purification. Ultraviolet light purification is more potent at destroying viruses like hepatitis and norovirus than chlorine disinfection and kills them instantly.
How UV Light works to purify water
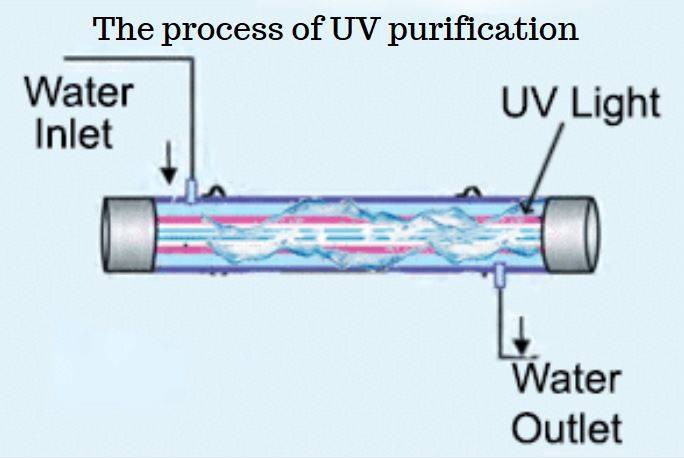
The frequency or intensity of the ultraviolet light determines the potency of killing organisms. When the intensity is high, the more effective it is at eliminating pathogens.
The ultraviolet light is scaled in a chamber, then the water runs throw the chamber and all the harmful viruses and bacteria die instantly the moment they are exposed to the ultraviolet radiation channel.
These ultraviolet systems of water purification are very effective and there is a guarantee that they kill 99.99% of microorganisms.
The UV light doesn’t affect the water since there is no strange odor or taste detected. However, UV radiation does not eliminate particles and heavy metals but removes all the bacteria, parasites, and viruses.
3. Filtration
Water filtration is a method commonly used in the purification of water for personal consumption, due to its ease of use and versatility. Systems of water filtration come in various sizes and forms, some of them being portable. The most common systems of water filtration are joined with refrigerators and household sinks by connecting them to the waterline.
How to Easily Filter Water at Home
The filter’s pore size, normally measured in microns, determines what is filtered through. The standard size of a micron of approximately 0.2 is small enough to block heavy metals like copper and lead as well as large parasites like cryptosporidium; however, does not block viruses.

Filtration systems normally use activated carbon as well as charcoal arranged in a round or cylindrical block; these porous materials absorb contaminants easily from the water.
As the water runs through the carbon, contaminants, and chemicals, stick to the carbon, allowing only the pure water to flow and pour into the basin of the filtration system.
Active carbon is very effective in eliminating several chemicals from the water. Studies indicate that filtration of water is capable of removing twelve types of herbicides and fourteen types of pesticides from water. Additionally, carbon eliminates bad odor produced by chlorine-treated water.
The filtration method removes: Bacteria, sediment, some heavy metal particles, and large parasites
4. Using Reverse Osmosis
The process of reverse osmosis forces water down a semi-permeable membrane to remove contaminants. Osmosis is a process that occurs naturally whereby the less concentrated solution, like freshwater, tends to flow towards the more concentrated solution, like seawater. The difference in both concentration levels is the saltwater molecules that are in the seawater.
How does the Process of Reverse Osmosis Work?
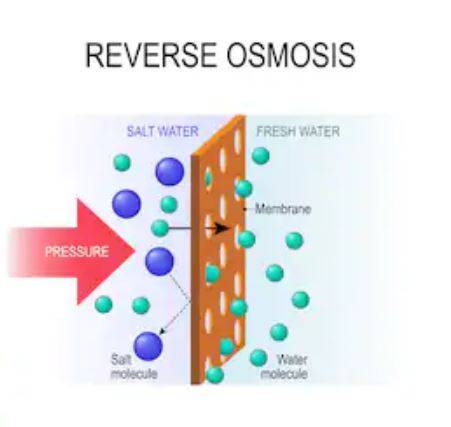
With eternal pressure, there is a reversal of the process, allowing the solution that is more concentrated to flow toward the solution with a lower concentration.
The semi-permeable screen allows only smaller molecules to go through, saltwater molecules don’t pass through while the freshwater goes through, and hence the result is clean, pure water, free from all contaminants.
Since the semi-permeable membrane usually filters particles at the molecular level, reverse osmosis is very effective at eliminating viruses, bacteria, and parasite cysts like cryptosporidium and Giardia.
The same can be used to purify borehole water from heavy metals like mercury and lead, and hard water minerals like magnesium, calcium, arsenic, and fluoride. However, it does not remove solvents and pesticides that are too small to go through the membrane.
Can Reverse Osmosis Remove Pesticides and Solvents from Water
Yes, pesticides and solvents can be eliminated from drinking water through granulated activated carbon or reverse osmosis. Reverse osmosis systems are small systems placed close to the kitchen sink.
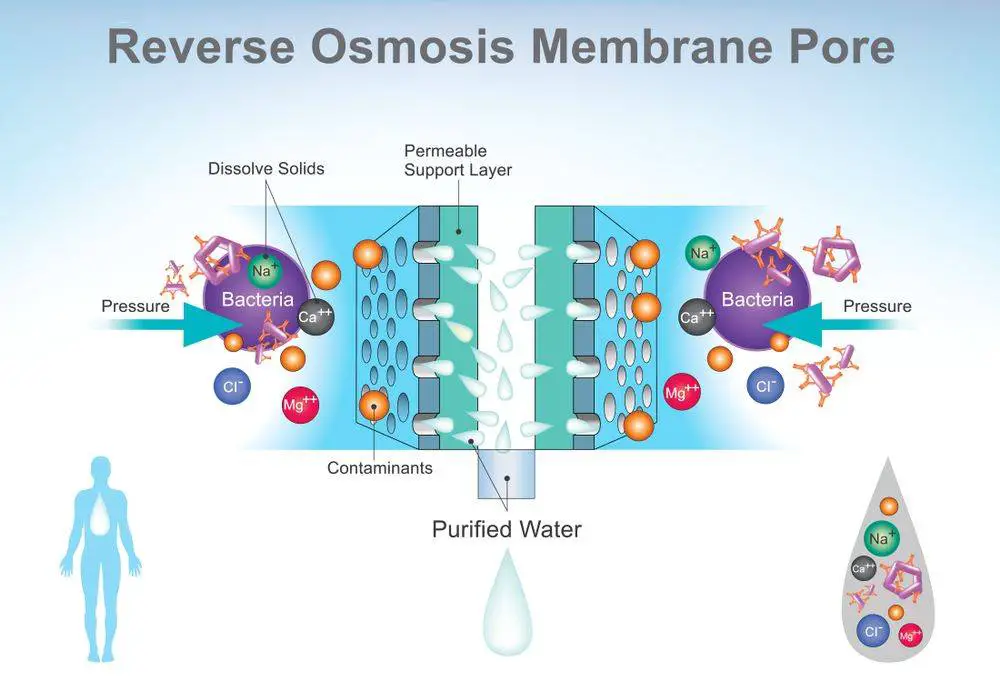
The system works by forcing water down a membrane. It only allows water molecules to go through, and blocks larger molecules and ions; like those that are associated with pesticides, solvents, ions, or lead.
5. Solar Purification
In the absence of traditional purification methods, solar purification is the most effective process. The ultraviolet rays from the sun are very effective in destroying viruses and bacteria.
A famous misconception about stagnant pond water safety is that the heat from the sun kills any dangerous microbes that are in the water. The truth is that stagnant ponds should be considered unsafe. This is because the water underneath the surface is a breeding ground for mosquitoes and bacteria.
One way of disinfecting water by solar purification is by using sunlight and plastic bottles. Remove all papers and labels from the bottles making sure they don’t have scratches.
How does Solar Purification Work?
Fill the bottles with water three-quarters full, then shake them for a period of half a minute for the activation of oxygen, then add water to fill them to the brim, cover, and lay them horizontally exposing them to direct sunlight
To achieve the best results, place the water bottles in direct sunlight and keep them uninterrupted for more than six hours. However, if it is cloudy, increase the exposure time to two days.
The solar still is a device that is constructed for distilling contaminated water into drinking water. It is also used for pulling condensation from damp resources to produce enough drinking water.
A solar still is a life-saving device when you are lost at sea without water or stranded in the forest without water. It is a simple device that uses the sun to evaporate contaminated water from the storage basin and gathers the condensation into another basin.
It can also apply to saltwater when constructed to suck moisture from the earth if the water is not available at all. These solar stills are either made from simple materials or bought to be used for emergencies. The solar purification system removes bacteria and viruses.
6. Povidone Iodine Water Purification
Iodine is a salt component that functions as a powerful disinfectant that prevents typhoid. It is a reddish-orange chemical that kills viruses and bacteria at the cellular level. It is available in the forms of tincture, tablet, liquid or crystal. Iodine purifies water by killing pathogens.
It kills Giardia cysts if left to sit for 50 minutes other than the standard 30 minutes. However, it’s ineffective against cryptosporidium. Iodine is very strong, and it is lethal in high doses.
Therefore it should be used for the purification of water when there is no other method available. Children, pregnant women, and those with iodine allergies or thyroid problems should not use it.
How to Purify Water using Iodine
To purify water using tincture iodine, add two drops of iodine to a quart jar of clear water, in case the water is foggy add ten drops. Allow the solution to stand for 30 minutes and allow the iodine to do its job. Note that the flavor of the water will change.
If you use a tablet or crystal iodine, follow the instructions from the manufacturer, one pitcher of crystal iodine will treat 2000 quarts. Always store iodine in a dark bottle since it is reactive to light.
Like chlorine, iodine also comes in tablet form, which makes them convenient and easy to carry. Iodine treatment removes Giardia, bacteria, and viruses; however, it doesn’t remove cryptosporidium.
7. Using Distillation
Distillation is the procedure used to collect condensed water from the evaporated steam. It is an effective means of making sure your water is free from all contaminants. Historically, the distillation method has been used as a purification method from as early as 200 AD by the Greeks. They used to distill seawater into fresh drinking water.
Throughout history, many cultures have used the distillation method to ensure potable water, although the distillation materials used have changed with time. However, science is still the same, giving proof that distillation is a method of purification that can be trusted.
How to Distill Water
The materials required in distilling water are a container for collecting the condensation, a boiling pot, a heat source, a tube for allowing the vapor to pass through, and a source of heat. When the water starts boiling, the vapor goes through the tube and pours into a new container.
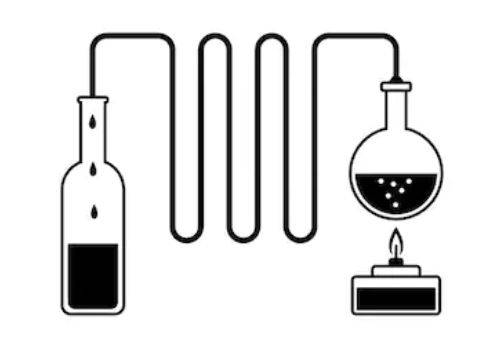
Since contaminants can not live in the form of steam, the “new “water is without viruses, bacteria, parasites chemicals, solvents, and particles. Since distillation is a very effective process, it also removes the essential minerals together with the contaminants from water; however, you can supplement the natural minerals by adding them to the water or by eating a diet rich in minerals
Home distillation units that are built on the countertop can be purchased locally. They are made from stainless steel grade 304, and most of these units distill water at the rate of four gallons in a day. The distillation process removes viruses, bacteria, parasites heavy metals, and impurities.
8. Purification by Boiling

Boiling water is the oldest method of water purification, and it’s still the most common today, not only in remote areas but also in urban areas. Boiling water long enough generates enough heat to destroy all types of pathogens, giving safe drinking water.
Using the law of pasteurization, a process used in making milk safe for drinking, most pathogens can not live in temperatures beyond 70 degrees centigrade, so long as the water boils long enough.
How Does Boiling Purify Water?

In case the water is murky, consider filtering the big contaminants using a coffee filter or clean cloth. Bring the water to a boil by heating it.
When the water starts to bubble, it is an indicator that the boiling water has reached one hundred degrees. Allow it to continue boiling for one minute.
After boiling, allow it to cool and store it in a clean bowl and cover tightly to avoid the re-contamination of microbes and bacteria. At the same time, not all bacteria like Clostridium do survive the boiling water. Luckily, this one is not life-threatening to human beings.
While boiling is effective in killing bacteria and purifying water, boiled water has a flat taste, emptying the water from one bowl to another will improve the taste. Boiling water removes viruses, bacteria, and parasites.
9. Using Sedimentation with Coagulation
When suspended water solids are colloidal or fine in shape, chemicals are usually used to remove the suspended matter. The coagulants react together with the murky particles, thereby forming a flocculent precipitate. Alum is a common coagulant that revolts against the water’s alkalinity to form aluminum-hydroxide floc.
If there is no required alkalinity in the water, soda ash lime may be introduced together with alum to achieve proper flocculation. Sometimes, activated silica is added to the water to give nuclei for the floc formation. In the process, colloidal suspensions that are finely divided are converted to solids which are can set through agglomeration.
The single floc particles clash with one another, and flocs of higher size are formed. However, these flocs grow slowly in quiescent water. Flocculation increases through gentle agitation of water to multiply the collision rate.
Violent agitation is dangerous as the flocs get disintegrated by the accelerated shear forces that are produced. The normal dosage of alum is 10-40mg/l.
The solid particles are removed by the process of sedimentation from water such as sand, silt, and larger microbes, however, smaller microorganisms and clay do not settle and hence can not be removed by sedimentation.
How to Remove Clays and Smaller Microbes from Drinking Water
Clay particles which range from about 0.2-2.0 microns are too small for cartridge sediment filtration. A micro-filtration process which uses a membrane that has smaller pore sizes can remove clay and small microbes to make your water safe for drinking.

The other way that water is purified from such is through sedimentation. The easiest process of sedimentation is by using rectangular tanks that have horizontal flow passing through them.
The water that has particles in suspension is poured from one of the ends of the tank, and then while the water is flowing through to the end of the other tank, the particles that are in the water settle.
10. Using Adsorption to Purify Water
Adsorption is the surface phenomenon that has a mechanism for removing inorganic and organic pollutants. When a solution with absorbable solute meets a solid with an extremely permeable surface structure, forces of attraction of liquid-solid intermolecular cause the solute molecules out of the solution to get deposited or concentrated on the solid surface.
In addition, the solute left behind in the adsorption process will be called adsorbate, while adsorbent is the solid that it is retained in the water. However, some contaminants may go through violent exothermically with the adsorbent, which is an explosion danger.
This surface collection of the adsorbate on adsorbent is known as adsorption. The creation of this adsorbed phase with a composition that is different from the one of the bulk fluid phase facilitates the separation through adsorption technology.
In the bulk material, most of the bonding requirements such as covalent, ionic, or metallic, of the integral atom of this material are loaded by various atoms on the material.
At the same time, the adsorption process mostly uses activated carbons, both powdered and granular activated carbons. They are common adsorbents that remove undesirable taste, color, and order as well as various inorganic and organic impurities.
The impurities removed
The two types of impurities come from industrial and domestic wastewater since they have a large surface area. The materials used can be locally available, so it can be a method to be used to purify water at home.
Moreover, the organic impurities they remove are such as dyes that are used by paper, pulp, and paper industries, phenols, pesticides and herbicides, organic solvents, alcohols, surfactants, phthalates, and hydrocarbons.
They are also used as non-volatile and semi-volatile chlorinated organic pollutants. These organic pollutants are easily removed by activated carbons clay minerals and clays through the adsorption process.
11. Using Low-Pressure Membranes
Filtration through the low-pressure membrane for the treatment of source water started developing at the beginning of the 1980s. During that time low-pressure membrane was used as nonchemical disinfectants for the food-processing industry.
Later on, in the late 1980s, various research projects were started by water utilities on the West Coast such as the Water Works Association of America Research Foundation, and various organizations to verify UF and MF for the municipals’ surface water treatment.
How Does Low-Pressure Membrane Purify Water?
Both Ultrafiltration and Microfiltration are filtration processes of the low-pressure membrane, and their operating principles are similar: pressure pushes the water across the membrane element as the pollutants that are larger than the size of the pores are retained.

The microfiltration membrane rejects particulates, bacteria, and suspended solids while Ultrafiltration rejects solids and some macromolecules such as emulsified oils.
The systems make it more automated compared with other methods of purifying water.
These systems concentrate on oily wastewater reducing the wastewater`s volume that is to be disposed of off-site. The ultrafiltration membrane pores are about1/10th the size of the microfiltration membrane pores.
The use of the hollow fiber membrane facilitates for reliable rejection of viruses, bacteria, suspended solids, and microorganisms.
12. Using Water Filters to Remove Inorganic Impurities
Minerals are present in industrial wastewater and also in foods and water for human consumption. Trace concentrations in the waste increase flora’s growth in receiving waters, the same way they increase the health and growth of humans who digest the water and foods. However excess minerals in receiving water stress the people who drink the water.

Therefore environmentalists need to differentiate between acceptable and excessive mineral content.
Phosphates, chlorides, and nitrates are the most common and significant examples of inorganic dissolved solids.
Several methods in the purification process
Among the methods used in removing the inorganic matter from water and wastes are dialysis, algae, ion exchange, reverse osmosis, evaporation, and miscellaneous methods.
Evaporating waste shows many problems, such as concentration changes during foaming, evaporation, scale formation temperature sensitivity, and the evaporator construction materials used. Evaporation efficiency is related to the heat-transfer rate. However, dialysis is the most efficient in getting pure solutions for manufacturing process reuse.
In reverse osmosis, two types of membranes are used; these are polyamide hydrazide or aromatic polyamide. Ion exchange is a new application used in waste treatment taken from the traditional method of softening water.
It is used mostly when the highest quality of water is required; however, it involves reactions of complex chemicals, hence requiring careful supervision and operation at all times. Sewage effluents are treated using algae. It is worth noting that some filters, such as the Brita Filters may not remove every impurity.
Also Read: Portable Sinks with Hot Water: Best Sink Units for Outdoors
How to Purify Water at Home by Removing Inorganic Impurities
1. How to Remove Iron from Water
Before treating water for iron, you need to know what type and source of iron you are treating. If the source of iron has corrosion, you should raise the water’s PH, or consider drilling your borewell deeper. Depending on the iron concentration in the water, more than one method of removal can be used according to a report from Ohio State University.
Consider installing the mechanical water softener in case the iron concentration is three parts for every million or less. Mechanical water softeners exchange iron with sodium through a process known as ion exchange. This process increases sodium in the water, which is not good for people living with high blood pressure.
Selecting filter and pH
Select an oxidizing or a greensand filter if the concentration of iron is three to ten ppm (parts per million). Greensand filters normally filter out iron through green clay material, Choose a filter that is of a good size, a filter that is too small for use with household water demand shall let the untreated water containing iron go through,
At the same time, if the PH of the water is less than 6.8, the water must run through the calcite filter first to raise the PH. Install a filtration and chlorination system for above 10 ppm concentrations. These systems are placed on top of the main pipe of water before it goes into the home.
The two-part systems add chlorine into the water first, usually the one that resembles common laundry bleach. A report from Ohio State University states that chlorine oxidizes the iron and kills iron bacteria, causing it to precipitate from the water where it’s removed through the filtration system.
Also Read: 12 Best Portable Bathtubs: Safe for Adults, Kids and Seniors
How to Remove Heavy Metals from Water at Home
The contamination of heavy metals is an increasing concern in today’s world. Inadequate wastewater and water treatment, together with heightened industrial activity, have contributed to the increase of heavy metals pollution in lakes, rivers, and various sources of water in developing countries.
However, methods of eliminating heavy metals from various water sources include activated carbon adsorption, electro-coagulation, and membrane filtration.
Things to Consider Before Buying Water Filters
Before buying a water filter, it is advisable to have your tap water checked for various contaminants. There are various water test kits for use at home to check if there are lead or certain heavy metals in your water. In case the test reveals heavy metals are present in your water, what do you do?

If your property has worn-out water pipes that have not been replaced in a long time, they will corrode. The metal corrosion will cause your water to have a high presence of heavy metals.
Therefore, changing your water pipes would be the best option to protect yourself against heavy metal poisoning. The pipes also need regular checks and maintenance to prevent corrosion.
However, old pipes aren’t the main source of contaminants, and testing your water can still reveal heavy metals present in your water even without old pipes in your plumbing. Some contaminants will be eliminated from drinking water by boiling; heavy metals can not be removed by boiling.
Why Boiling Water is not Safe to Remove Metals
Why boiling water is not safe to remove metals because it increases the concentration of the metals. Boiling water with heavy metals increases their concentration. Unfortunately, heavy metals are undegradable and quite indestructible, which makes them a hard contaminant to remove.
Small children and pregnant women are the ones at risk of heavy metal poisoning. However, a diet rich in iron and calcium will slow down the rate of absorption of heavy metals. The best defense against heavy metals poisoning is to minimize exposure to the heavy metals.
Using Water Filters to Remove Metals from Water

Installing water filters that remove heavy metals is the safest and best line of defense from these contaminants.
One of the best water filters that you can fit in your water systems at home is the Kinetic degradation fluxion( KDF)
KDF filters work by reducing an oxidation reaction in removing water-soluble cations of mercury, lead, nickel, copper, chromium, and various dissolved metals.
As the water goes through the media of the KDF, soluble heavy metals are changed to soluble atoms, which are later electroplated onto the filter media. This filter can remove 98% of water-soluble heavy metals.
Also Read: 12 Best Bathtubs for Seniors & Walk-In Tubs for elderly shower
How to Purify Water by Removing Chlorine
The point-of-use water filter is mostly recommended for chlorine removal from water. This filter is a granular activated carbon filter made from organic materials that are raw like wood, coal, and coconut shells. Heat is used to activate the carbon, which increases the surface area.
This big surface area, joined with the natural porous properties of carbon, makes it efficient at trapping and absorbing odors, and tastes of synthetic organic chemicals and all-natural organic compounds from the water that goes through.
A polyphosphate filter used together with the point-of-use system is also recommended for the removal of chlorine from drinking water. When polyphosphate particles dissolve the coating around chemicals like calcium, magnesium, and iron, it helps in removing the impurities.
This is done by making it difficult for these agents to continue staying in water after it has been filtered and ready to be dispensed for drinking. Learn more about how to purify water by removing chlorine from drinking water on that post.
How to Remove Fluoride from Water
Water filters are the best method applied to remove fluoride from the water safely at home. A reverse osmosis system of filtration is the most efficient method of removing fluoride from your drinking water. This system can eliminate 85-92% of fluoride from water. In reverse osmosis technology, household water pressure is used to push the tap water across the filtration process.
The water goes down a semi-permeable membrane and additional filters like carbon filters or sediment. Reverse osmosis eliminates fluoride and other various contaminants like sulfates, pesticides, lead, asbestos, and detergents.
Currently, above 15 million organic compounds have been listed in the chemical abstracts, and all of them are likely to be found in water, hence, an exhaustive analysis of organic compounds in the water will remain a difficult undertaking. However, we have seen hundreds of methods of water purification by removing organic and inorganic impurities, hence there is no reason why you should take contaminated water.
To learn more about this, read our guide on removing fluoride from water. Apply the purification methods listed in this write-up and have safe drinking water for your family or community.
How to Remove Cryptosporidium from Drinking Water
To inactivate or kill cryptosporidium from drinking water, Boil water for about one minute, allow it to cool, then store it in a sanitized clean container that has a tight cover and keep it in the refrigerator.
Other than boiling, you can use a point-of-use filter. However, not all filters can remove cryptosporidium. Filters designed to remove cryptosporidium must have these labels:
- Reverse osmosis
- Absolute pore acreage of one micron or lesser
- Tested and verified by NSF 53 standard for cyst reduction or removal
How to Remove Cyclosporum from Drinking Water
Cyclosporum is a bowel infection caused by cyclospora cayetanensis, a tiny parasite usually found in contaminated fruits, vegetables, and water with human feces.
To stay free from this parasite drink bottled water, and avoid putting ice in drinks, make sure the food you eat is steaming hot, wash your hands with water and soap after using the toilet. This parasite cannot be removed by bleaching or chlorine; however, intense water treatment can remove it.
Also Read: 10 Best Bedside Commodes: potty chairs for seniors & handicapped
Conclusion
Each of the methods discussed has its own merits and demerits. At the same time, different methods have their cost implications. Of all these methods, boiling water remains the most simple and highly effective.
However, just like all other methods, boiling may not remove inorganic impurities. This calls for a combination of other water purification methods to guarantee that the water is safe for drinking.
While there are several methods to purify water for drinking, there are a number of them that can be implemented at home. the 12 methods we have explored are not only simple but also easily implemented at home or in a small office.
Watch how to set up simple DIY distillation and purify water at home or away.


I am a homeowner excited by various innovative products and solutions that make life better. I am happy to share such ideas and reviews of home and related products.